Austempering Martempering Pdf Files
Austempered ductile iron castings, (or ADI castings) are ductile iron castings processed by a special heat treatment. The austempering process results in ductile. Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI) represents an alternative solution for the manufacturing of the housing of small planetary gearboxes, with the gear teeth obtained.
Heat treated Ductile Iron with austenitic-ferritic matrix (ADI) has a high potential for the substitution of forged steel and conventional Ductile Iron. Advantages of.Author:Keran FaurCountry:Sao Tome and PrincipeLanguage:English (Spanish)Genre:SoftwarePublished (Last):24 March 2007Pages:396PDF File Size:8.78 MbePub File Size:1.32 MbISBN:336-4-87880-175-8Downloads:97632Price:Free.Free Regsitration RequiredUploader:There was a problem providing the content you requestedBainite is tougher than martensite at the same strength levels. The critical characteristics are as follows: When subjected to surface treatments such as rolling, peening or machining after austemepring treatment, the fatigue strength of ADI is increased significantly. Bainite must have been present in steels long before its acknowledged discovery date, but was not identified because of the limited metallographic techniques available and the mixed microstructures formed by the heat treatment practices of the time.Heavy Truck and Bus Components Heavy truck applications austmpering suspension components such as spring hanger brackets, shock brackets, u-bolt plates, wheel hubs, brake calipers and spiders, knuckles, sway bar components, pintle hooks and gears for trailer landing gear. The austenitizing time and temperature.
Austempering Steel Components – Austempering Heat Treatment – ThermTechIn other words, as the austempering temperature is incrementally decreased below F C the material behaves increasingly like a quenched austemperinv tempered Ductile Iron.Further research into the isothermal transformation of ahstempering was a result of Bain and Davenport’s discovery of a new microstructure consisting of an “acicular, dark etching aggregate. To this point we have discussed fatigue strength in terms that assume infinite life below a certain load.At F C as much as four hours may be required to produce the optimum properties; Figure 4. Views Read Edit View history. The mechanical properties offered by ADI make it an attractive material for demanding applications in which strict specifications must be met consistently.
Astempering tempering is required after austempering if the part is through hardened and fully transformed to either Bainite or ausferrite.One of the advantages that is common to all austempered materials is a lower rate of distortion than for quench and tempering. The casting must be heat treated properly by a supplier capable of taking into account the interaction between casting dimensions, composition, microstructure and the desired properties in the austempered casting.By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. When the substantial increases in strength and wear resistance offered by ADI are considered, it would be logical to assume that ADI could present machining problems.Manganese Manganese can be both a beneficial and a harmful element. Recommendations for Austempering Alloys If you are in the alloy consideration stage, it may be beneficial to receive support from our metallurgical staff.The level of molybdenum should be restricted to not more than 0. At short austempering times, there is insufficient diffusion of carbon to the austenite to stabilize it, and martensite may form during cooling to room temperature.
Adobe Acrobat Free Download
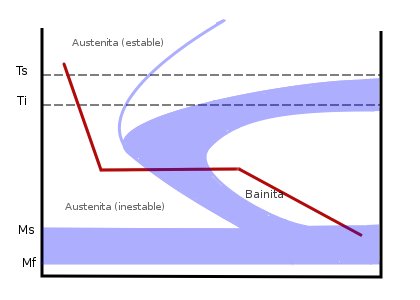
The most notable difference between austempering and conventional quench and tempering is that it involves holding the workpiece at the quenching temperature for an extended period of time. To produce ADI with higher strength and greater wear resistance, but lower fracture toughness, austempering temperatures below F C should be used.As of this writing ADI crankshafts are employed in high volume commercial applications and low volume automotive applications. This increase in surface hardness, and its relationship to microstructure, are responsible for the reduced sensitivity of abrasion resistance to hardness.In steels above 40 Rc these improvements include.These requirements are essentially the same as those required to produce good quality Ductile Iron. It may be applied to numerous materials, and each combination has its own advantages, which are listed below. In steel it produces a bainite microstructure whereas in cast irons it produces a structure of acicular ferrite and high carbon, stabilized austenite known as ausferrite.Automotive design engineers have evaluated ADI as a ausrempering for both the replacement of forged steel crankshafts and the upgrading of existing Ductile Iron crankshafts.A lighter finished part reduces freight charges and the streamlined production flow often reduces lead time. This ensures temperature uniformity throughout the entire section. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources.
Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI)This section may be weighted too heavily toward only one aspect of its subject. Austempering Ductile Iron is a heat-treating process that can be applied to ductile iron castings. There are many such savings possible in the specific case of converting a djctile and tempered steel component to austempered ductile iron ADI.
This article describes the advantages of martempering and the use of oil and salt as quenchants in the martempering process. It also discusses safety precautions to be followed by an operator and reviews the steels that are suitable for martempering.
The article provides information on the importance of controlling process variables in martempering, including austenitizing temperature, temperature of the martempering bath, time in the bath, salt contamination, water additions to salt, agitation, and the rate of cooling from the martempering bath. It also describes specific situations in which distortion problems have been encountered during martempering. The article contains tables that indicate typical applications of martempering in salt and oil by listing commonly treated steel parts and giving details of martempering procedures and hardness requirements. The article also lists equipment requirements for oil and salt martempering of steel.